This can also be clearly seen from the MCU shipments. According to IC Insights statistics, the global MCU product shipments will increase from 22.1 billion in 2015 to 36.1 billion in 2020, and even reach 39.5 billion in 2021. particles. The market size has also grown rapidly in the past two years of shortages and price increases. The market size in 2020 is 19.7 billion US dollars, and it will increase by 11% to 21.5 billion US dollars in 2021. It is expected to continue to grow this year.
After more than 30 years of development in the domestic MCU market, both the market and product technology have also been greatly developed. In terms of market size, according to IHS statistics, the domestic MCU market has grown from 18 billion yuan in 2015 to 26.9 billion yuan in 2020. The application market includes automotive electronics (33%), industrial control and medical care (25%) , computers (23%), consumer electronics (11%), etc.
The development history of MCU
The history of MCU's appearance is not long, but its development is very rapid. In 1971, Hoff of Intel Corporation of the United States developed the world's first 4-bit microprocessor chip 4004, marking the advent of the first generation of microprocessors. At the time, the 4004 was equipped with RAM, ROM and shift registers, contained 2300 transistors, had dimensions of 3mm x 4mm, and was originally sold for $200. Then, in 1972, Intel launched the 8-bit microprocessor Intel8008, and the 8080 with a main frequency of 2MHz and a 6-micron process, and the number of transistors increased by 6,000.
In addition to Intel's MCS-48 series of MCUs, Zilog also developed the Z80 microprocessor in 1976, which is widely used in microcomputers and industrial automatic control equipment. At the time, Intel, Motorola, and Zilog were the three major players in the microprocessor field.
In 1980, on the basis of MCS-48 series MCU, Intel launched MCS-51 series 8-bit MCU (the most typical high-performance 8051 MCU), which caused quite a stir in the field of industrial control, and quickly established its unshakable position. MCS-51 series MCUs have greatly improved in terms of on-chip RAM capacity, I/O interface functions, and system expansion.
Soon after, Intel completely opened up the technology of 801 MCU, which attracted many semiconductor manufacturers in the world to join the army of developing and transforming 8051 MCU. Among them, Philips has made great contributions, which has focused on the development of the control function and peripheral units of the microcontroller; Atmel has implanted FlashROM inside the MCU, which makes the application of the MCU more flexible; the ADUC8xx series MCU launched by ADI, in the MCU to It has played a very important role in the development of SoC.
In 1983, Intel launched a high-performance 16-bit microcontroller MCS-96 series, with more advanced technology and more integrated transistors, up to more than 120,000. In addition to Intel, TI, Atmel, Microchip, Renesas, etc. have also launched 16-bit MCU products.
Before 2000, MCU companies basically used self-developed cores. After that, as computing requirements became more and more complex, core manufacturers began to appear, and the division of labor was further refined. MCU manufacturers began to use outsourced cores and put their main energy into peripheral circuits, etc. development of other parts.
At present, among the third-party MCU cores, the ArmCortexM series is dominant. This series is developed by Arm and takes the form of IP authorization. The Cortex-M series has the design characteristics of short pipeline and ultra-low power consumption. In 2004, Arm introduced its first Cortex-M series processor, the M3, and ST was the first to adopt it and quickly launched a series of 32-bit MCUs based on this core.
Of course, in addition to the MCU cores of the Cortex-M series, there have also been many companies specializing in providing IP in the RISC-V that has emerged in recent years, and many domestic MCU companies have launched related products. Next, let's take a look at the mainstream MCU core IP on the market.
Mainstream MCU core IP
At present, both domestic and foreign, Arm's Cortex-M series MCU cores are mainstream. Up to now, Arm has launched a total of 10 Cortex-M series MCU core IP, which can meet the needs of low, medium and high-end. Among them, M0, M0+, M1, M23 four series are low-end MCU core IP; M3 and M4 are mid-end MCU core IP; M7, M23, M35P, M55 are mid-to-high-end MCU core IP products.
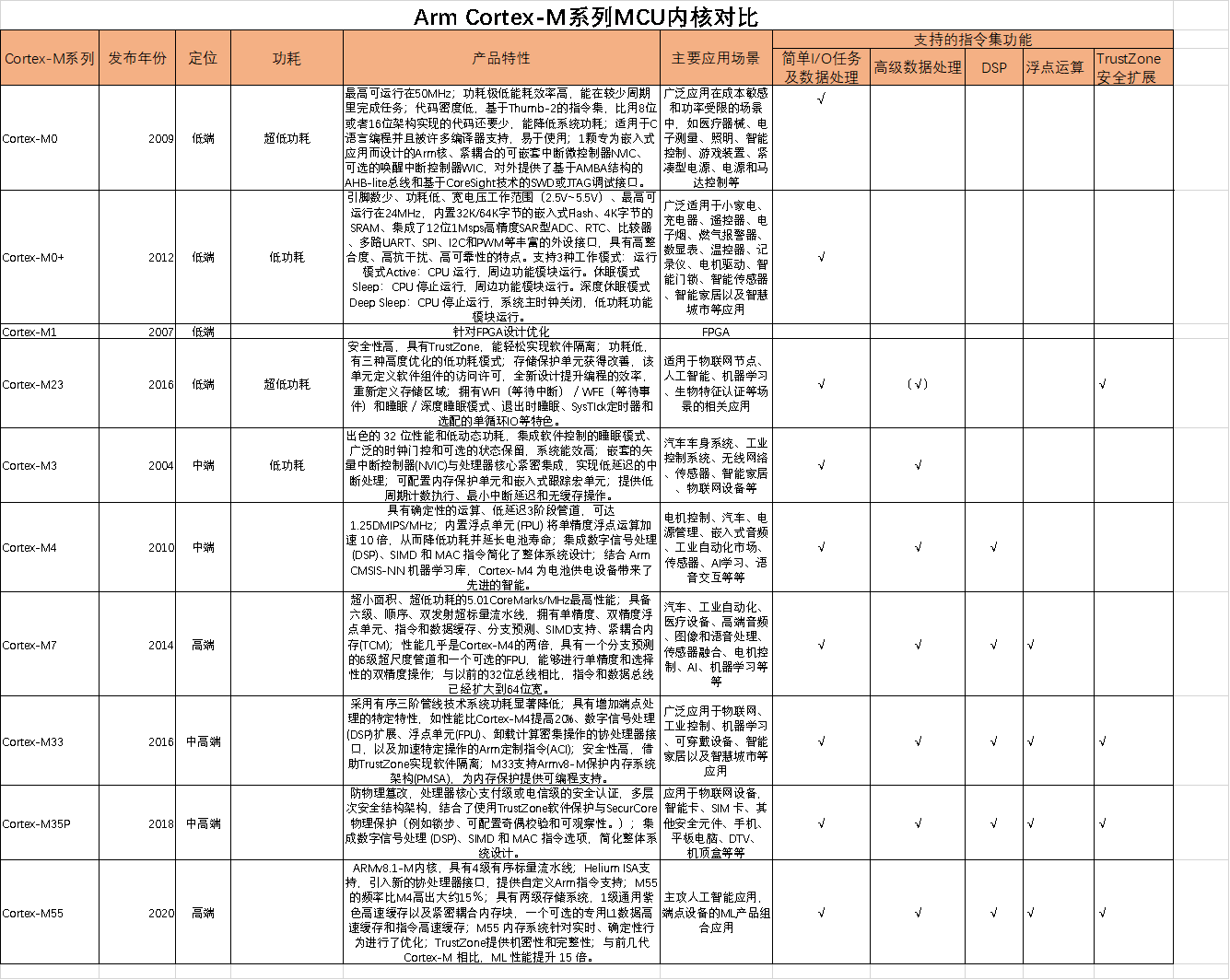
Among foreign manufacturers, Renesas mainly focuses on self-developed cores, accounting for nearly 80% of the product numbers of self-developed cores; except for more than half of Microchip's self-developed core MCU products, most other manufacturers mainly use Cortex-M series MCU cores , and they have a layout in low, medium and high-end products.
90% of domestic MCU manufacturers have adopted Arm's Cortex-M series cores. Different from foreign manufacturers, domestic MCU manufacturers are basically concentrated in several product series. Among them, Zhaoyi's innovative 32-bit MCU products mainly use five MCU cores: M23, M3, M4, M33 and RISC-V; Huada Semiconductor mainly uses two MCU cores, M0+ and M4; National Technology mainly uses M0 and M4. M4 has two MCU cores. In addition, its M7 core MCU products are still under development; Zhongying Electronics mainly focuses on 8-bit MCUs, and its 32-bit MCUs use M3 cores; Chipsea's 32-bit MCU products use M0 Core; BYD Semiconductor's 32-bit MCU products use M0 and M0+; Smart Microelectronics mainly uses M0, M0+, M3, and Arm China STAR-MC1 cores.
In recent years, RISC-V has been very popular in China. Although there are not many companies that have launched RISC-V core MCU products, the future potential is still good. Now in the RISC-V market, SiFive, Andes Technology, Pingtou Ge, and Xinlai Technology all have corresponding IP products.
In addition to these third-party MCU core IP products, many manufacturers' self-developed core products are still developing, such as Renesas' RXv1, RXv2, and RXv3 series cores; Microchip's PIC16, PIC32, AVR DB, AVR DA, etc. MCU core. There are also MCU companies with self-developed cores in China, such as the KungFu8 and KungFu32 cores of Xinwang Microelectronics.
Although the mainstream of the market is already 32-bit MCU, there is still a certain market for 8-bit MCU, and many MCU companies are still launching new 8-bit MCU products. At present, in the 8-bit MCU market, Microchip dominates with a market share of more than 30%, followed by NXP with about 15%; in addition, Renesas and ST also occupy about 10% of the market share.
Most of these 8-bit MCU manufacturers use self-developed cores. For example, Microchip mainly uses AVR and PIC cores; NXP mainly uses RS08 and M68HC cores; Renesas mainly uses RL78, H8 and 78K0; ST uses STM8 kernel.
In addition to self-developed cores, 8-bit MCU manufacturers will also use 8051 open source cores to develop products. Earlier we mentioned that the 8051 core is an architecture developed by Intel in 1980. After losing patent protection in 1998, it became an open source IP, which once again showed a strong secondary vitality. Certain changes have been made, and various differentiated products have been introduced. But such products are basically collectively referred to as 8051 core MCU. At present, domestic manufacturers using the 8051 core include Zhongying Electronics, Hongjing Technology, BYD Semiconductor, Chipsea Technology, and Fuman Microelectronics.

