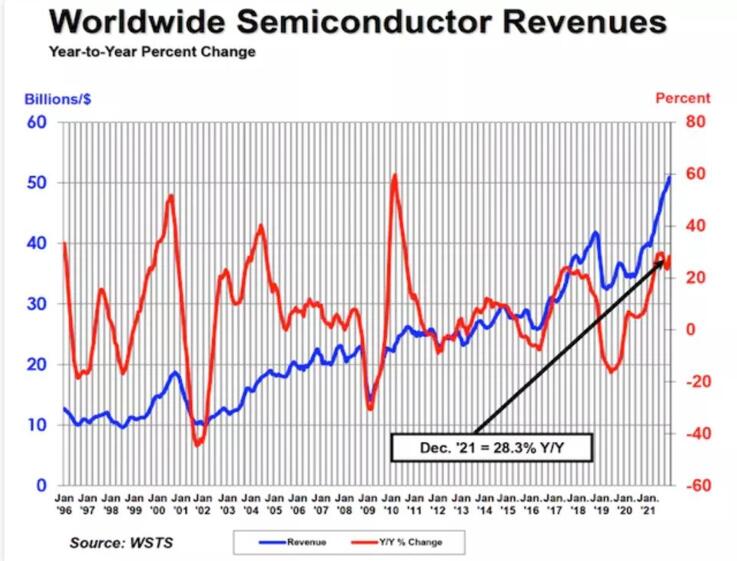
Image via SIA
Sheng Linghai, vice president of research at Garnter, told the media, "The current market has shifted from a general shortage to a partial shortage." He pointed out that there is no shortage of 5G mobile phone chips, and the production capacity of 28nm process chips has gradually been able to keep up with market demand. Judging from the types of chip shortages in the current market, there are still shortages in many fields including PCs, servers, automobiles, and industry, but the degree of shortages has improved compared to 2021.
On February 9, according to Taiwanese media reports, industry sources revealed that as demand continues to outstrip supply, the tight supply of WiFi core chips is not expected to ease significantly in 2022, although suppliers are seeking more from foundry partners. Capacity support, but the delivery period will continue to maintain a long state. WiFi6/6E core chips are mostly manufactured using 28nm process. This is by far the most popular process node, but supply is very limited. The shortage of WiFi core chips is not expected to improve until more new 28nm capacity comes online in 2023.
The 28nm process has been used in the industry for more than 10 years. In recent years, TSMC, UMC, SMIC, and NSMC have all expanded their production capacity at the 28nm node. Why is it favored around the 28nm process? Will the expansion of production capacity in the future solve the dilemma of lack of cores? After the expansion of production capacity is in place in the future, will it cause overcapacity? In order to understand the specific situation of the industry, the author interviewed Lv Jianxin, executive vice president of the Guangdong Semiconductor Association, and industry professionals to interpret the latest progress of the 28nm process.
28nm process node development history and application scenario expansion
The 28nm process is the first mass production started by TSMC in 2011. When it is turned on, it has a learning hegemony system. This process is the most profitable and the most dominant process era in the history of TSMC's development. In 2011, Qualcomm, AMD, and Nvidia took the lead in applying the 28nm process. GPU, graphics processor chips are beginning to use this process. Product performance has been greatly improved, and these companies have made money quickly. Since then, they have been out of control.

Figure: TSMC process evolution diagram, the picture comes from TSMC's official website
Lv Jianxin, executive vice president of Guangdong Semiconductor Association, told reporters that 28nm is a process that is less affected by China's stuck neck. Taking SMIC as an example, the company's 28nm technology was launched in the fourth quarter of 2013 and started in 2015. Mass production of 28nm process was carried out, and in 2018, it announced the completion of the research and development of 28nm HKMG, which is also the first enterprise in mainland China capable of mass production of 28nm process. This process is relatively mature for domestic wafer foundries. At present, domestic expansion is mainly based on 28nm.
Lv Jianxin said: "28nm is of strategic significance for fabs in mainland China. Because some key materials and equipment are affected by geopolitical factors, the probability of China's implementation of high-end processes such as 14nm, 7nm, and 5nm is low. The 28nm process is a domestic expansion. Second, the current maturity of 28nm in industry applications, including price, yield and efficiency, is favored by the industry. Compared with 40nm and 55nm, the profit margin is relatively high, and 28nm is in the middle of performance and cost. It can be said that it is the most cost-effective and mainstream process in the current wafer process. Third, in addition to high-end consumer electronics (mobile phone SoC, computer chips, high-end data center chips), 28nm process chips are overwhelmingly It is sufficient for most application areas.
Industry experts revealed to reporters: 28nm has become a mainstream process node for mature processes. One comes from market demand. 28nm is not only a logic process, but also derives many characteristic processes. For example, 28HP, 28LP with low power consumption, 28HPL with high performance and low power consumption, and 28HPM with high performance computing technology. There are also more choices in materials, and even a fab has developed an FDSOI process. 28nm is not a process, but a family that can correspond to different application needs. The more mature and mainstream process platforms are, the more promising they are.
The second is driven by technology. The next process of 28nm is 22nm. The industry has adopted the FinFET structure invented by Chinese scientist Mr. Hu Zhengming. The 22nm process is based on High-K (high-K) gate dielectric + Metal Gate, which reduces leakage while increasing pipeline control. At present, many chip design companies and mainstream foundries are investing heavily into 28nm for process expansion and research and development.
Third, from the perspective of investment, many products are currently migrating to 28nm. For example, display driver chips are a large market, and they are still growing rapidly every year, digesting a large part of the production capacity of fabs. In particular, some complex MCUs have also begun to use the 28nm process, so there are more and more chip products in the 28nm process.
The consensus in the semiconductor industry is that 28nm chips are seen as a bridge between the low end and the high end of integrated circuit manufacturing capabilities. In addition to the relatively high power consumption required by CPU, GPU and AI chips, most industrial-grade chipsets use 28nm or higher chipsets, and chips with 28nm process technology are used in a wide range of products including TVs, air conditioners, automobiles , high-speed rail, industrial robots, elevators, medical equipment, smart bracelets, drones. Industry watchers expect China to become self-sufficient in 28nm manufacturing this year, paving the way for increased production of 14nm chips.
The three major conditions for the expansion of 28nm production in the five fabs have become the key to the implementation of production capacity
At present, the global chip foundries can be divided into three levels. The first level is the two top foundry manufacturers TSMC and Samsung. The technology has reached 5nm, and this year it will enter 3nm. The second level is UMC, GF, and SMIC, and the technology has reached 14nm; the third level is Hua Hong, PSMC and other manufacturers, and the technology has only reached 28nm. At present, TSMC and Samsung are actively competing for orders for advanced manufacturing processes, and the expansion is mainly based on advanced manufacturing processes such as 7nm and 5nm. , the third-level process is more mature, competing for orders above 90nm.
According to Omdia data, 2013 was the year of popularization of the 28nm process, and between 2015 and 2016, the 28nm process began to be widely used in mobile phone application processors and basebands. With the maturity of technology, the market demand for 28nm process products has shown an explosive growth trend, and this high growth trend will continue until 2017.
Just because the 28nm at that time was too "attractive", it attracted many manufacturers to increase their layout. In 2018, media reports have indicated that the global 28nm has a pattern of overcapacity, and TSMC, UMC, etc. are facing the crisis of overcapacity. Even, TSMC once said when reviewing its Q3 performance in 2018 that the current global overcapacity problem of 28nm is serious, and it will be in a situation of oversupply in the next few years. Since then, 28nm capacity has started to decline.
Since 2021, with the advancement of the "home economy" caused by the new crown epidemic, the global demand for consumer electronics and cloud services such as tablet computers, 5G mobile phones, and PCs has soared. The demand for chips for new energy vehicles is 3-4 times higher than that of traditional vehicles. The demand for chemical chips has brought about a global shortage of chips. The capacity of chip foundries cannot keep up with the rapidly growing demand.
In response to chip supply shortages, chipmakers are aggressively ramping up production capacity, with global wafer shipments increasing by 14% year-on-year in 2021. At present, chip manufacturers are focusing on solving the shortage of cutting-edge chips. According to data from the American consulting firm McKinsey, in 2021, the production capacity of chips using old technologies such as 40nm technology will increase by 4%, and the production capacity of chips using new technologies such as 28nm technology will increase by 13%. %.
Global 28nm capacity expansion map
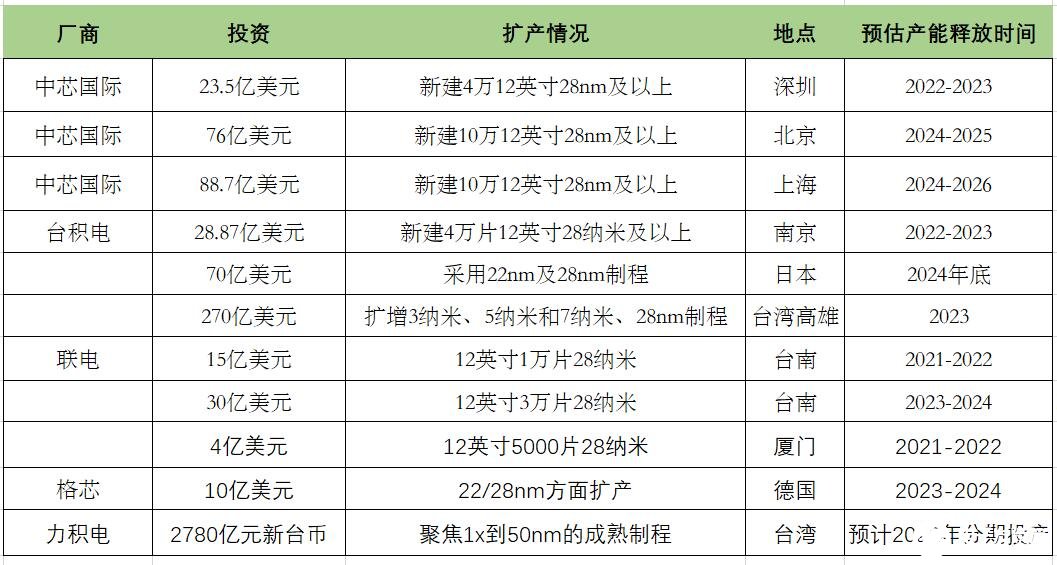
Figure: Electronic enthusiasts draw according to public information
For the expansion of the 28nm process, the fab has to solve three key issues: capital, customers and the supply of semiconductor equipment.
Since the second half of last year, new factories of chip foundries have become popular to bind IC customers with long-term contracts, so as to avoid unclaimed production capacity in case of oversupply in the environment after new production capacity is opened. The benefits of this model are mainly two points: one is to ease the financial pressure of chip foundries to expand production, and the other is to bind customers to obtain stable orders without worrying about idle production capacity; it is also a great benefit to cooperative IC design customers. It can ensure the supply of future production capacity at a stable price.
TSMC proposes a plan to invest 40 billion US dollars in capital in 2022. In addition to the capacity expansion in 2nm, 3nm, 5nm and 7nm, TSMC's 28nm 12-inch factory in Kumamoto, Japan will expand production together with major customers such as Sony. Production will begin in late 2024. In addition, TSMC is expected to start offering 28nm manufacturing services at its Nanjing plant in the second half of 2022. TSMC also plans to build a new factory in Kaohsiung, Taiwan, where additional 7nm and 28nm chip production lines will be set up, with production scheduled to start in 2024.
UMC spent more than 3 billion US dollars to expand production. UMC pointed out that the long-term contract binding rate of 28nm process capacity is as high as 80%. Even if the 28nm market turns to oversupply, the company will be limitedly affected. Its contract customers include Qualcomm, Samsung Electronics, MediaTek, Novatek, Realtek, Qijing, Yili, and Phison.
SMIC, a major domestic chip foundry, has a capital expenditure plan of US$5 billion this year. In terms of 12-inch wafer fab expansion, SMIC has simultaneously launched the expansion of new factory projects in Shanghai Lingang, Beijing and Shenzhen. Zhao Haijun, CEO of the company, said that only a small amount of the newly built production capacity is reserved for potential customers in development, and the platform, technology and price of other production capacity have been negotiated. The company has also signed some long-term contracts LTA, and receives prepayment. As for customers, SMIC will give priority to binding with leading customers.
Another constraint in the expansion of production is the delivery time of semiconductor equipment. Equipment transactions are too long, resulting in slow 28nm expansion. According to semiconductor equipment manufacturers, the current popular 28nm and other process-related equipment delivery times have not been shortened, and there are few suppliers or sophisticated advanced process equipment. The delivery time is also long. Exclusive EUV equipment must be reserved at least 2-3 years in advance. Now we can only actively prepare inventory, optimize related processes, and fully reduce the work schedule.
At present, the 28nm process platform will have huge market demand in the next 10 years. A mobile phone may use more than 100 chips, and a car may use more than 1,000 chips, but not all chips are as fast and thin as processors, and the most advanced technology is used. Most applications The end chip only needs a mature process, so the 28nm process with cost-effective advantages will always exist.
Warning! Will 28nm chips be oversupplied in the future?
At present, the design cost of chips continues to rise. According to data, the average design cost of 28nm chips is about 30 million US dollars, 16nm/14nm chips are about 80 million US dollars, and 7nm chips need 271 million US dollars. The high cost causes only a few IC design companies. Affordable to move to premium nodes.
Lv Jianxin, executive vice president of the Guangdong Semiconductor Association, told reporters that the semiconductor field has been a cyclical industry since its birth. The world's five major fabs have expanded their production to 28nm, and the surplus after the expansion is inevitable. China's semiconductor industry and China's electronic information industry are in a period of golden development opportunities. The production capacity of domestic 28nm chips is currently unable to support the domestic market demand. To solve the problem of chip shortage, a sustainable way out is to expand production capacity. He especially emphasized that in this round of global wafer manufacturers' expansion, TSMC, Samsung, and European chip companies mainly expanded their production with advanced processes below 14nm, and Chinese fabs mainly expanded their production with mature processes of 28nm and above. Considering its huge market demand, relatively speaking, the problem of excess chips in the Chinese market will be less than in other markets.
Recently, Jason Wang, co-general manager of UMC, told the media that the 28nm process market segment may be oversupplied after 2023. "Based on the announced capacity expansion plans, we do think the 28nm oversupply will occur after 2023. But we still think the oversupply will be mild."
Zhao Haijun, CEO of SMIC, recently told the media that the potential 28nm overcapacity issue that the market is worried about can be considered from two aspects: First, the company has not built too much production capacity in the past, and now the company's expansion will not be shaken until the entire market becomes Oversupply; second, industrial transfer. Now many customers are bundled with the system and the whole machine for inspection. From another perspective, a large part of the components must be produced in China, so in the future, there may be an oversupply in some regions and insufficient production capacity in some regions.



